How to Create a Simple Chat App with Microsoft Agent Framework
I’ve recently started exploring the new Microsoft Agent Framework, and workflow approach like it is in LangGraph looks great. To get a hands-on feel for the framework, I decided to start with a simple project: a console-based chat application.
This article documents my steps in creating this simple chat app. It’s a great way to understand the core concepts of the framework, like setting up agents, defining workflows, and handling user input in a loop.
Initial setup
- Create a new console application using the .NET CLI:
dotnet new console -n SimpleChatApp
cd SimpleChatApp
- Add the necessary NuGet packages. The core of our application will use the
Microsoft.Agentframework, and for this demo, I’m usingOllamaSharpto connect to a local LLM (https://ollama.com/).
You can add these packages via the CLI:
dotnet add package Microsoft.Agents.AI --prerelease
dotnet add package Microsoft.Agents.AI.Abstractions --prerelease
dotnet add package Microsoft.Agents.AI.Workflows --prerelease
dotnet add package OllamaSharp
- Csproj file:
<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk">
<PropertyGroup>
<OutputType>Exe</OutputType>
<TargetFramework>net9.0</TargetFramework>
<ImplicitUsings>enable</ImplicitUsings>
<Nullable>enable</Nullable>
</PropertyGroup>
<ItemGroup>
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.Agents.AI" Version="1.0.0-preview.251028.1" />
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.Agents.AI.Abstractions" Version="1.0.0-preview.251028.1" />
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.Agents.AI.Workflows" Version="1.0.0-preview.251028.1" />
<PackageReference Include="OllamaSharp" Version="5.4.8" />
</ItemGroup>
</Project>
Code
- Initialize the
OllamaApiClientandChatClientAgentto connect and use local LLM (in this case,gemma3:4b).
var uri = new Uri("http://localhost:11434");
using IChatClient chatClient = new OllamaApiClient(uri, "gemma3:4b");
- Define a
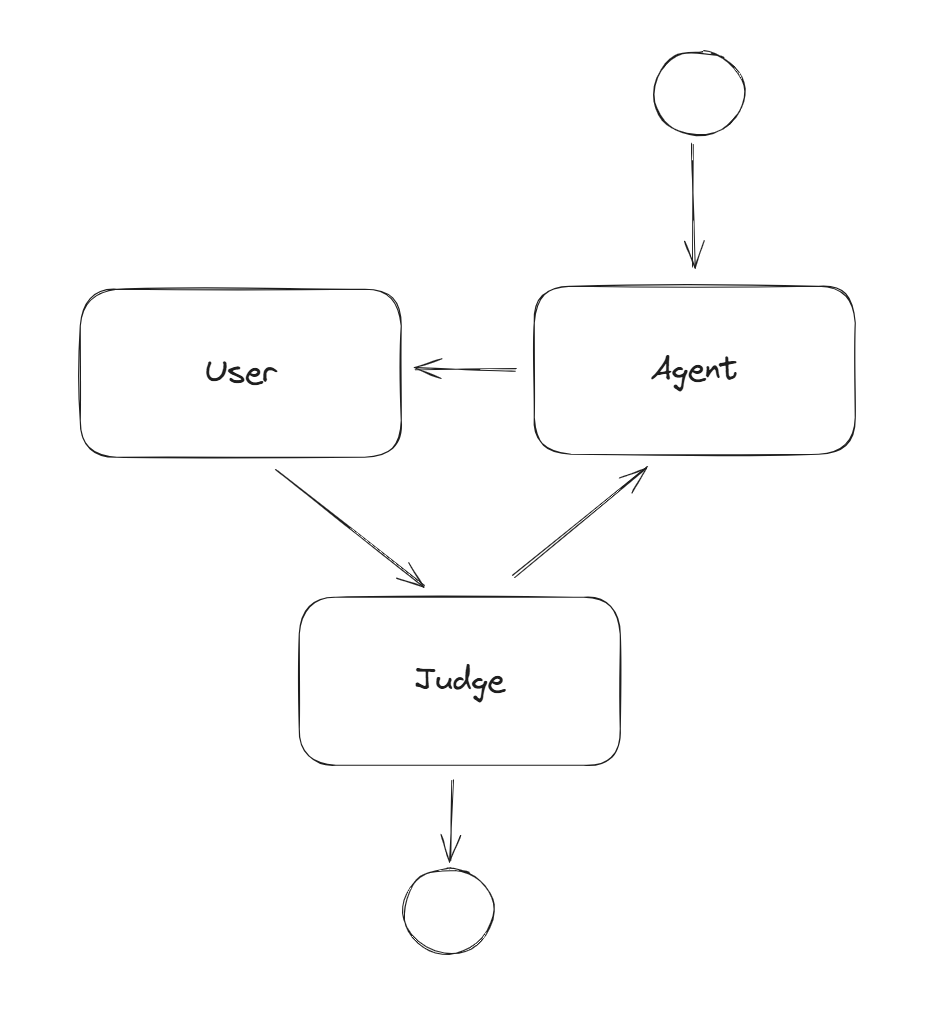
Workflowthat orchestrates the interaction between the user and the agent. This workflow is a simple loop.
var workflow = new WorkflowBuilder(conversationAgent)
.AddEdge(conversationAgent, inputPort)
.AddEdge(inputPort, judgeExecutor)
.AddEdge(judgeExecutor, conversationAgent)
.WithOutputFrom(judgeExecutor)
.Build();
- Add a
JudgeExecutorwhich is a custom component to decide if the conversation should continue or end based on user input. A key part of this component is sending aTurnTokento pass control back to the agent after the user provides an answer.
internal sealed class JudgeExecutor() : Executor<JudgeInput>("JudgeExecutor")
{
public override async ValueTask HandleAsync(JudgeInput input, IWorkflowContext context, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(input.Message))
{
await context.YieldOutputAsync($"Done!", cancellationToken);
}
else
{
List<ChatMessage> updatedMessages = [..input.Messages, new ChatMessage(ChatRole.User, input.Message)];
await context.SendMessageAsync(updatedMessages, cancellationToken: cancellationToken);
await context.SendMessageAsync(new TurnToken(emitEvents: true), cancellationToken: cancellationToken);
}
}
}
- The main loop streams events, prints messages, and waits for the user to type a response. The code for
AgentRunUpdateEventis commented out, but you can uncomment it to see all the intermediate updates from the agent as it processes.
await foreach (WorkflowEvent evt in handle.WatchStreamAsync())
{
switch (evt)
{
case RequestInfoEvent requestInputEvt:
var data = requestInputEvt.Request.DataAs<List<ChatMessage>>() ?? [];
foreach (var chatMessage in data)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{chatMessage.Role}: {chatMessage.Text}");
}
// Handle human input request from the workflow
await handle.SendResponseAsync(requestInputEvt.Request.CreateResponse(new JudgeInput(Console.ReadLine(), data)));
break;
case WorkflowOutputEvent outputEvt:
// The workflow has yielded output
Console.WriteLine($"Workflow completed with result: {outputEvt.Data}");
return;
// case AgentRunUpdateEvent agentRunUpdate:
// Console.WriteLine($"{agentRunUpdate.ExecutorId}: {agentRunUpdate.Data}");
// break;
}
}
- Full code:
using Microsoft.Agents.AI;
using Microsoft.Agents.AI.Workflows;
using Microsoft.Extensions.AI;
using OllamaSharp;
var uri = new Uri("http://localhost:11434");
using IChatClient chatClient = new OllamaApiClient(uri, "gemma3:4b");
AIAgent conversationAgent = new ChatClientAgent(chatClient, new ChatClientAgentOptions(instructions: "You are a conversation agent."));
RequestPort inputPort = RequestPort.Create<List<ChatMessage>, JudgeInput>("UserInput");
var judgeExecutor = new JudgeExecutor();
// Build the workflow by connecting executors in a loop
var workflow = new WorkflowBuilder(conversationAgent)
.AddEdge(conversationAgent, inputPort)
.AddEdge(inputPort, judgeExecutor)
.AddEdge(judgeExecutor, conversationAgent)
.WithOutputFrom(judgeExecutor)
.Build();
// Execute the workflow
await using StreamingRun handle = await InProcessExecution.StreamAsync(workflow, new ChatMessage(ChatRole.User, "Hello, how are you?"));
await handle.TrySendMessageAsync(new TurnToken(emitEvents: true));
await foreach (WorkflowEvent evt in handle.WatchStreamAsync())
{
switch (evt)
{
case RequestInfoEvent requestInputEvt:
var data = requestInputEvt.Request.DataAs<List<ChatMessage>>() ?? [];
foreach (var chatMessage in data)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{chatMessage.Role}: {chatMessage.Text}");
}
// Handle human input request from the workflow
await handle.SendResponseAsync(requestInputEvt.Request.CreateResponse(new JudgeInput(Console.ReadLine(), data)));
break;
case WorkflowOutputEvent outputEvt:
// The workflow has yielded output
Console.WriteLine($"Workflow completed with result: {outputEvt.Data}");
return;
// case AgentRunUpdateEvent agentRunUpdate:
// Console.WriteLine($"{agentRunUpdate.ExecutorId}: {agentRunUpdate.Data}");
// break;
}
}
internal sealed class JudgeExecutor() : Executor<JudgeInput>("JudgeExecutor")
{
public override async ValueTask HandleAsync(JudgeInput input, IWorkflowContext context, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(input.Message))
{
await context.YieldOutputAsync($"Done!", cancellationToken);
}
else
{
List<ChatMessage> updatedMessages = [..input.Messages, new ChatMessage(ChatRole.User, input.Message)];
await context.SendMessageAsync(updatedMessages, cancellationToken: cancellationToken);
await context.SendMessageAsync(new TurnToken(emitEvents: true), cancellationToken: cancellationToken);
}
}
}
record JudgeInput(string? Message, List<ChatMessage> Messages);