Ai900 Ml Types
create a blog post based on page content. Provide markdown code to copy paste. Do not add any source or reference links to it.
What is Machine Learning and How Does It Work?
Machine learning is a branch of artificial intelligence that enables computers to learn from data and make predictions without being explicitly programmed. Machine learning can be used for various tasks, such as recognizing faces, diagnosing diseases, recommending products, and playing games.
But how does machine learning work? What are the different types of machine learning and how are they applied? In this blog post, we will answer these questions and give you a brief overview of the main concepts and techniques of machine learning.
Types of Machine Learning
There are multiple types of machine learning, and you must apply the appropriate type depending on what you’re trying to predict. A breakdown of common types of machine learning is shown in the following diagram.
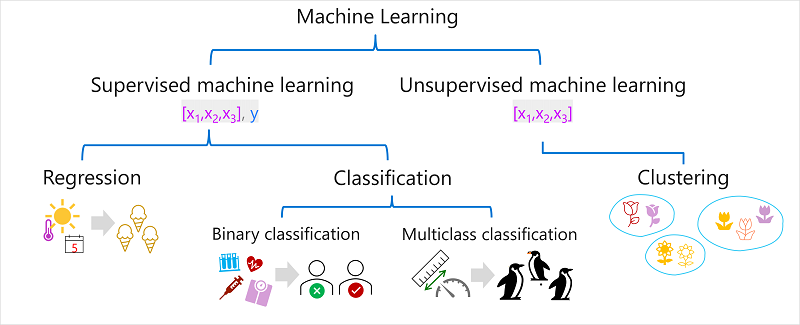
Supervised Machine Learning
Supervised machine learning is a general term for machine learning algorithms in which the training data includes both feature values and known label values. Features are the attributes or variables that describe the data, such as height, weight, color, etc. Labels are the outcomes or targets that we want to predict, such as price, category, rating, etc.
Supervised machine learning is used to train models by determining a relationship between the features and labels in past observations, so that unknown labels can be predicted for features in future cases.
There are two main subtypes of supervised machine learning: regression and classification.
Regression
Regression is a form of supervised machine learning in which the label predicted by the model is a numeric value. For example:
- The number of ice creams sold on a given day, based on the temperature, rainfall, and windspeed.
- The selling price of a property based on its size in square feet, the number of bedrooms it contains, and socio-economic metrics for its location.
- The fuel efficiency (in miles-per-gallon) of a car based on its engine size, weight, width, height, and length.
Regression models can be linear or nonlinear, depending on the complexity of the relationship between the features and the label. Some common regression algorithms are linear regression, polynomial regression, decision tree regression, and neural network regression.
Classification
Classification is a form of supervised machine learning in which the label represents a categorization, or class. There are two common classification scenarios.
Binary Classification
In binary classification, the label determines whether the observed item is (or isn’t) an instance of a specific class. Or put another way, binary classification models predict one of two mutually exclusive outcomes. For example:
- Whether a patient is at risk for diabetes based on clinical metrics like weight, age, blood glucose level, and so on.
- Whether a bank customer will default on a loan based on income, credit history, age, and other factors.
- Whether a mailing list customer will respond positively to a marketing offer based on demographic attributes and past purchases.
In all of these examples, the model predicts a binary true/false or positive/negative prediction for a single possible class.
Multiclass Classification
Multiclass classification extends binary classification to predict a label that represents one of multiple possible classes. For example,
- The species of a penguin (Adelie, Gentoo, or Chinstrap) based on its physical measurements.
- The genre of a movie (comedy, horror, romance, adventure, or science fiction) based on its cast, director, and budget.
In most scenarios that involve a known set of multiple classes, multiclass classification is used to predict mutually exclusive labels. For example, a penguin can’t be both a Gentoo and an Adelie. However, there are also some algorithms that you can use to train multilabel classification models, in which there may be more than one valid label for a single observation. For example, a movie could potentially be categorized as both science fiction and comedy.
Some common classification algorithms are logistic regression, k-nearest neighbors, support vector machines, decision trees, random forests, and neural networks.
Unsupervised Machine Learning
Unsupervised machine learning involves training models using data that consists only of feature values without any known labels. Unsupervised machine learning algorithms determine relationships between the features of the observations in the training data.
The most common form of unsupervised machine learning is clustering. A clustering algorithm identifies similarities between observations based on their features, and groups them into discrete clusters. For example:
- Group similar flowers based on their size, number of leaves, and number of petals.
- Identify groups of similar customers based on demographic attributes and purchasing behavior.
In some ways, clustering is similar to multiclass classification; in that it categorizes observations into discrete groups. The difference is that when using classification, you already know the classes to which the observations in the training data belong; so the algorithm works by determining the relationship between the features and the known classification label. In clustering, there’s no previously known cluster label and the algorithm groups the data observations based purely on similarity of features.
In some cases, clustering is used to determine the set of classes that exist before training a classification model. For example, you might use clustering to segment your customers into groups, and then analyze those groups to identify and categorize different classes of customer (high value - low volume, frequent small purchaser, and so on). You could then use your categorizations to label the observations in your clustering results and use the labeled data to train a classification model that predicts to which customer category a new customer might belong.
Some common clustering algorithms are k-means, hierarchical clustering, density-based clustering, and Gaussian mixture models.
Conclusion
Machine learning is a powerful and versatile tool that can be used for a variety of tasks and applications. By understanding the different types of machine learning and how they work, you can choose the best approach for your problem and data. In this blog post, we have covered the basics of supervised and unsupervised machine learning, as well as some common algorithms and examples. We hope you have found this post informative and useful. If you want to learn more about machine learning, check out our online courses and tutorials.