Ai900 Computer Vision
Machine learning for computer vision
Computer vision is a branch of artificial intelligence that deals with extracting meaning from images. In this post, I will introduce some of the most common machine learning techniques for computer vision, and how they can be used to solve various tasks.
Convolutional neural networks (CNNs)
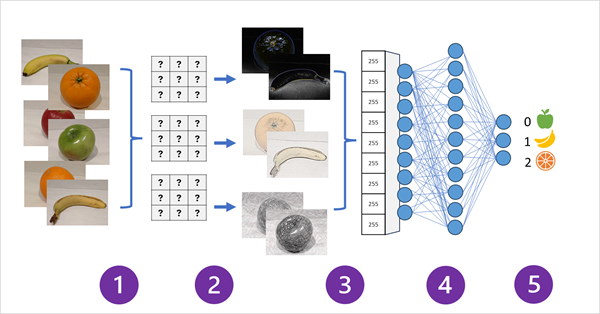
One of the most popular machine learning models for computer vision is a convolutional neural network (CNN). A CNN uses filters to extract numeric features from images, and then feeds them into a deep learning model to generate a prediction. For example, a CNN can be trained to classify images of different kinds of fruit, by learning the optimal filter weights that help identify the shape, color, and texture of each fruit.
A CNN consists of several layers, such as:
- Convolutional layers: These layers apply filters to the input image, producing feature maps that capture the presence of certain patterns in the image.
- Pooling layers: These layers reduce the size of the feature maps, making the model more efficient and robust to noise.
- Activation layers: These layers apply a non-linear function to the feature values, enhancing the model’s ability to learn complex relationships.
- Fully connected layers: These layers connect all the feature values to the output layer, where the final prediction is made.
The following diagram illustrates the basic structure of a CNN:
Transformers and multi-modal models
CNNs have been the dominant machine learning models for computer vision for a long time, but they are not the only ones. Recently, another type of neural network architecture, called a transformer, has emerged as a powerful alternative. Transformers were originally developed for natural language processing (NLP), where they encode words or phrases as vector embeddings, representing their semantic relationships in a high-dimensional space. Transformers can handle long sequences of data, and learn from large amounts of unlabeled data.
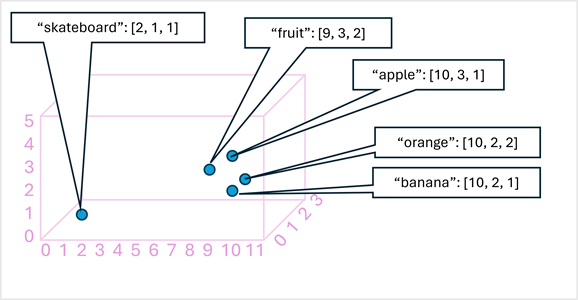
Transformers can also be applied to image data, by encoding pixel values or image features as embeddings, and learning the associations between them. This enables the creation of multi-modal models, which can process both text and image data, and generate outputs in either modality. For example, a multi-modal model can be trained to caption images, tag images, or generate images from text descriptions.
One of the most advanced multi-modal models is the Microsoft Florence model, which is trained on a large corpus of captioned images from the Internet. Florence can encode both text and image embeddings, and learn the relationships between them. Florence is a foundation model, meaning that it can be used as a basis for building adaptive models for specific tasks, such as image classification, object detection, or image generation.
The following diagram shows how a multi-modal model like Florence works:
Conclusion
Computer vision is a fascinating and rapidly evolving field of AI, with many applications and challenges. Machine learning models, such as CNNs and transformers, are the key to unlocking the potential of computer vision, by enabling computers to understand and manipulate images. In this post, I have given a brief overview of some of the most common and cutting-edge machine learning techniques for computer vision, and how they can be used to solve various tasks. I hope you enjoyed reading it, and learned something new. Thank you for your attention!